Cellulite is a common concern for many people, often becoming more noticeable as we age or go through changes in our body composition. Despite being a completely normal and harmless condition, it can still be a source of frustration and insecurity. This has led to countless questions and myths about how to reduce or eliminate it. One of the most asked questions is: Does cellulite go away when you get toned?
In this article, we will explore the science behind cellulite, examining how factors like muscle tone, body fat percentage, and overall lifestyle can impact its appearance. Whether you’re embarking on a new fitness journey or looking for effective ways to smooth out your skin, understanding the relationship between exercise, diet, and cellulite can help you set realistic goals and expectations.
Understanding Cellulite
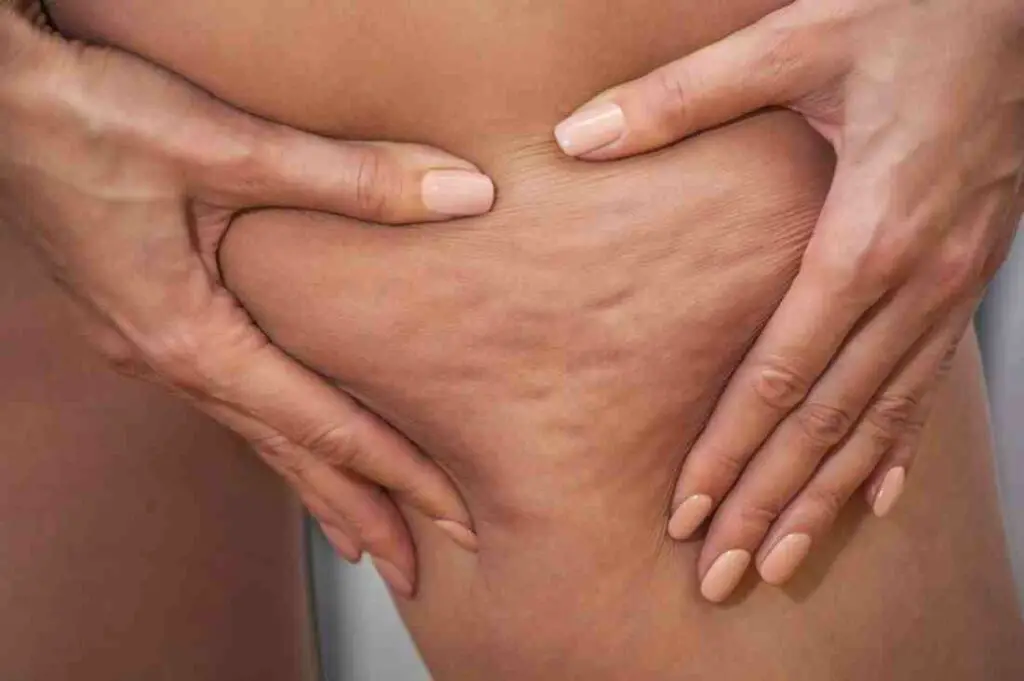
Cellulite is a common, non-medical term used to describe fat that appears bumpy because it pushes against connective tissue, causing the skin above it to pucker. This condition is not harmful and is seen more frequently in women than men due to differences in fat distribution, muscle, and connective tissue.
SHOP FOR THE RESISTANCE BAND ON AMAZON
Symptoms of Cellulite: Cellulite often presents as dimpled or lumpy skin, sometimes described as having a cottage cheese or orange peel texture. It’s most noticeable on the thighs, hips, and buttocks, but can also appear on the breasts, lower abdomen, and upper arms. The severity of cellulite can vary, with some individuals only showing signs when the skin is pinched, while others may have more visible cellulite even without pinching the skin.
Why Cellulite Occurs: The exact cause of cellulite is not fully understood, but it’s believed to involve the fibrous connective cords that tether the skin to the underlying muscle. As fat cells accumulate, they push up against the skin, while these cords pull down. This push-pull effect creates the uneven surface or dimpling characteristic of cellulite. Hormonal factors, genetics, weight, and muscle tone can all influence the development of cellulite. It’s more common in areas where women typically store fat, such as the thighs, hips, and buttocks.
Structural Differences Between Normal Fat and Cellulite: While all fat acts as an energy reserve, insulates our bodies, and provides cushioning, cellulite has a unique structure compared to regular fat. In women, fat cells and connective tissue are arranged vertically, which makes the fat cells push out and create that dimpled, puckered look. On the other hand, men’s connective tissue has a criss-cross pattern that holds fat more securely, making cellulite less common for them. However, as we age, connective tissue can weaken, and fat cells can push through, making cellulite more noticeable.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of cellulite can help individuals determine the best approach to managing its appearance. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Causes of Cellulite
- Fibrous Connective Cords: Cellulite forms when fibrous connective cords that tether the skin to underlying muscle pull down, while fat cells push up against the skin. This creates an uneven surface or dimpling.
- Fat Accumulation: While not solely a factor of excess fat, the way fat is distributed and stored in the body can influence the appearance of cellulite. This is more pronounced in areas where fat deposits are closer to the skin.
- Skin Structure and Thickness: The structure of the skin, including its thickness and elasticity, plays a role. Thinner skin can make cellulite more visible, while thicker skin can help mask it.
Risk Factors for Cellulite
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop cellulite than men due to differences in fat distribution, connective tissue, and hormonal influences. Women’s fat cells and connective tissue are arranged vertically, while men’s tissue has a crisscross structure, which is less prone to cellulite formation.
- Age: As people age, their skin loses elasticity and becomes thinner, which can make cellulite more noticeable. Additionally, hormonal changes related to aging can influence cellulite development.
- Genetics: Genetic factors influence the likelihood of developing cellulite. This includes metabolism, fat distribution, circulatory levels, and skin structure.
- Hormones: Hormones such as estrogen, insulin, noradrenaline, thyroid hormones, and prolactin play a role in the development of cellulite. Estrogen, in particular, can cause fat cells to enlarge and retain more fluid.
- Body Composition: Higher body fat percentages, regardless of weight, can increase the risk of cellulite. However, even lean individuals can develop cellulite.
- Smoking: Smoking affects blood flow and the formation of collagen, which can weaken the connective tissue and exacerbate cellulite.
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to increased fat storage and affect skin health, contributing to the formation of cellulite.
- Clothing: Tight clothing that restricts blood flow can potentially contribute to the development of cellulite by affecting circulation.
- Diet: People who eat too much fat, carbohydrates, or salt and too little fiber are likely to have greater amounts of cellulite.
SHOP FOR THE FOAM ROLLER ON AMAZON
In conclusion, while cellulite may not completely disappear with toning efforts, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management, can help minimize its appearance.
The Role of Toning
Muscle tone can significantly influence the appearance of cellulite. Cellulite occurs when underlying fat deposits push through the layers of collagen fibers or connective tissue beneath the skin, creating a dimpled or lumpy appearance. This is more common in areas where the body stores fat, such as the thighs and buttocks.
When muscles are well-toned, they are firmer and more defined. Toned muscles can provide better support for the skin and fat layers above them. This support can reduce the amount of fat that pushes against the skin, thereby making the cellulite less visible. Essentially, increased muscle tone can tighten the skin’s surface, leading to a smoother appearance.
Conversely, a lack of muscle tone can make cellulite more noticeable. Without firm muscle support, fat cells are more likely to bulge through the weakened connective tissue, accentuating the cellulite’s characteristic dimples. This is why individuals with a sedentary lifestyle, which often leads to reduced muscle tone, may see an increase in the visibility of cellulite.
Therefore, incorporating strength training and exercises that enhance muscle tone can be an effective strategy in managing the appearance of cellulite. While it may not eliminate cellulite completely, improving muscle tone can help reduce its prominence and improve the overall texture of the skin.
Weight Management
Weight loss and weight gain can both have noticeable effects on cellulite, albeit in different ways. When someone loses weight, especially if it’s a significant amount, there may be a reduction in the appearance of cellulite due to a decrease in the overall volume of fat cells. As fat cells shrink, the dimpled areas may become less prominent or even smoother, creating the illusion of reduced cellulite.
However, it’s essential to note that weight loss doesn’t necessarily eliminate cellulite entirely. Even individuals with low body fat percentages can still have cellulite due to factors like skin elasticity, collagen structure, and underlying muscle tone. So while weight loss may reduce the visibility of cellulite to some extent, it might not completely eradicate it.
SHOP FOR THE SKIN-FIRMING LOTION ON AMAZON
Conversely, weight gain can exacerbate the appearance of cellulite. When someone gains weight, the fat cells in their body expand, which can lead to increased pressure on the connective tissues beneath the skin. This pressure can cause the fat cells to protrude through the fibrous bands, resulting in more pronounced dimpling and cellulite. Additionally, certain types of weight gain, such as rapid weight gain or weight gain from unhealthy sources like processed foods, can further contribute to cellulite formation due to inflammation and poor circulation.
Exercise and Cellulite
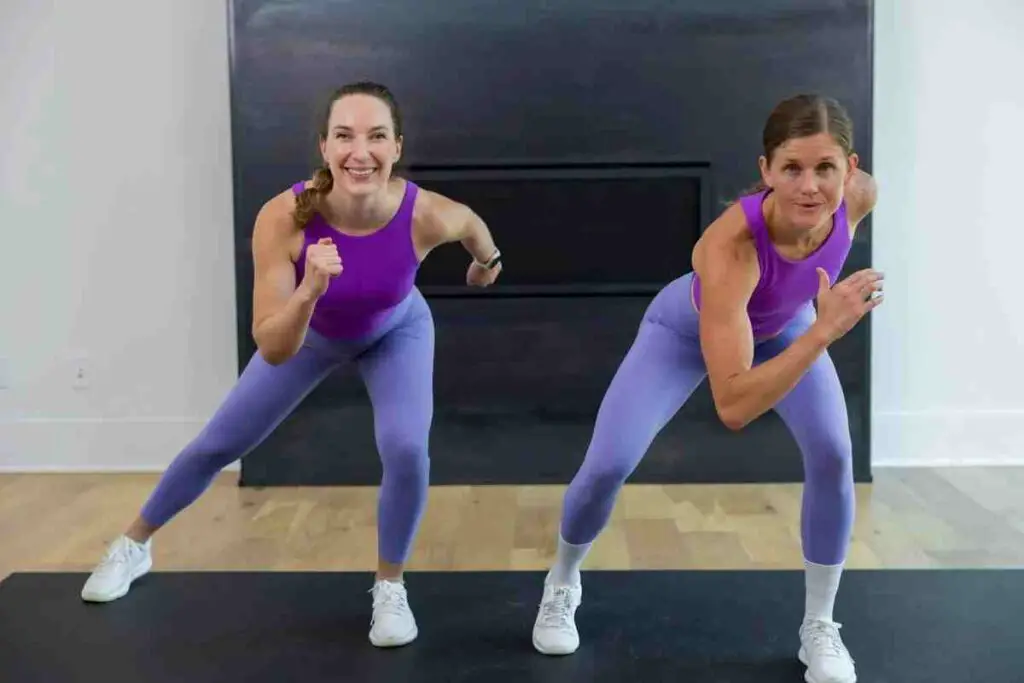

Reducing cellulite involves a combination of cardio exercises to burn fat and strength training exercises to tone and tighten muscles. Here’s a breakdown of the types of exercises that can help:
Target Muscles in Romanian Deadlift
Cardiovascular Exercises: Cardio exercises are effective at burning calories and reducing overall body fat, which can in turn decrease the visibility of cellulite. These exercises increase heart rate and metabolism, aiding in weight loss and fat reduction. Some effective cardio exercises include:
- Walking or Jogging: Easy to start and suitable for all fitness levels, walking and jogging can help burn fat and improve circulation.
- Cycling: Both outdoor cycling and stationary biking are excellent for toning the legs and reducing fat.
- Swimming: Provides a full-body workout and is especially good for those with joint issues.
- Jumping Rope: A high-intensity workout that can burn a significant number of calories.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Alternating short bursts of intense activity with periods of rest, HIIT can be more effective at fat burning compared to steady-state cardio.
Strength Training Exercises: Strength training helps build muscle, which can firm the areas affected by cellulite and improve skin texture. By increasing muscle tone, you also boost your resting metabolic rate, which helps burn more calories even when you’re not exercising. Some strength training exercises that target cellulite-prone areas include:
- Squats: They target the glutes, thighs, and hips, helping to build muscle and reduce fat in these areas.
- Lunges: Both forward and side lunges work the thighs and buttocks, improving muscle tone.
- Glute Bridges: Focus on the gluteal muscles and can help lift and firm the buttocks.
- Deadlifts: Work the entire posterior chain, which includes the hamstrings and glutes.
- Step-Ups: Great for targeting the thighs and glutes, and can be done with or without weights.
How These Exercises Help:
- Burning Fat: Cardio exercises like running, cycling, and swimming increase heart rate and calorie expenditure, leading to fat loss throughout the body, including cellulite-prone areas.
- Improving Circulation: Cardiovascular exercises enhance blood flow, which can help reduce fluid retention and improve the appearance of cellulite.
- Muscle Toning: Strength training exercises target specific muscle groups, increasing muscle mass and definition. This helps to firm and tighten the skin, reducing the dimpled appearance associated with cellulite.
- Boosting Metabolism: Both cardio and strength training exercises boost metabolism, leading to increased calorie burn even at rest, which contributes to overall fat loss and cellulite reduction.
Top Exercises for Glutes and Hamstrings
Combining these exercises into a balanced workout routine, along with maintaining a healthy diet and staying hydrated, can lead to significant improvements in reducing cellulite and achieving smoother, firmer skin.
Diet and Cellulite
Diet plays a significant role in managing cellulite by influencing skin elasticity and collagen production. Here’s how certain foods can help or hinder this process:
Effects of Skipping Hamstring Exercises
Foods That Improve Skin Elasticity and Collagen Production: Certain foods can help improve skin elasticity and boost collagen production, which can help reduce the appearance of cellulite:
- Vitamin C-rich foods: Foods like oranges, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli are high in vitamin C, which is vital for collagen production.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Foods like fish, walnuts, and chia seeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can improve skin elasticity.
- Protein-rich foods: Foods such as lean meat, poultry, fish, legumes, and dairy are high in protein, which is essential for collagen production.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Berries, dark chocolate, pecans, and artichokes are high in antioxidants, which can help protect collagen in your skin.
Foods That Can Contribute to Cellulite: On the other hand, certain foods can contribute to cellulite by leading to fat accumulation or inflammation:
- Processed foods: Foods that are high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats can lead to weight gain and inflammation, which can worsen cellulite.
- Refined carbohydrates: Foods like white bread, pasta, and baked goods can cause a spike in blood sugar, leading to fat accumulation.
- Unhealthy fats: Trans fats and saturated fats found in fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks can lead to weight gain and inflammation.
- Sugary beverages: Drinks like soda and sweetened coffee can lead to weight gain and inflammation, worsening cellulite.
SHOP FOR THE DRY BRUSH ON AMAZON
Incorporating foods that promote collagen production and skin elasticity while avoiding those that contribute to cellulite can be an effective strategy for managing its appearance. It’s also important to maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and engage in regular physical activity to support overall skin health.
Treatment Options
When it comes to managing cellulite, there are several treatment options available. These treatments aim to improve the appearance of cellulite, but it’s important to note that most do not offer permanent solutions. Here are some of the commonly used treatments for cellulite:
- Topical Treatments: Creams and lotions containing caffeine or retinol may help to temporarily tighten the skin and make cellulite less noticeable.
- Massage and Manual Manipulation: Techniques like Endermologie involve massaging and rolling the skin to improve circulation and lymphatic drainage, which may temporarily reduce the appearance of cellulite.
- Laser and Radiofrequency Treatments: These treatments heat the skin and disrupt the connective tissue, which can lead to a temporary reduction in cellulite. Some laser treatments also promote collagen production, which may improve skin texture.
- Acoustic Wave Therapy: Sound waves are used to break up cellulite, which may reduce its appearance after several treatment sessions.
- Subcision: A procedure called Cellfina™ involves inserting a needle under the skin to break up the fibrous bands causing cellulite dimpling. This can lead to a smoother skin appearance that may last for two years or more.
- Vacuum-assisted Precise Tissue Release: This method cuts the tough bands beneath the skin that cause cellulite, allowing the tissue to move upward and fill out the dimpled skin. The results may last up to three years.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can make cellulite less visible, as excess fat can exacerbate the appearance of cellulite.
Individuals interested in these treatments need to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, to discuss the best options based on their specific condition and to understand the potential risks and benefits.
FAQs
Q 1. What is the earliest age cellulite can appear?
Ans. Cellulite can begin to appear after puberty, with the earliest onset often occurring in the teenage years. Hormonal changes during this time can contribute to its development.
Q 2. Can men get cellulite, and if so, how common is it?
Ans. While less common than in women, men can also develop cellulite. The distribution of fat, muscle, and connective tissue in men typically makes cellulite less visible.
Q 3. Is cellulite only a cosmetic issue, or can it have health implications?
Ans. Cellulite is primarily a cosmetic concern and does not pose any health risks. However, its presence can sometimes affect an individual’s self-esteem and body image.
Q 4. Are there any specific vitamins or supplements that can help reduce cellulite?
Ans. Vitamins that support skin health, such as Vitamin C and E, may help improve skin elasticity and potentially reduce the appearance of cellulite. However, there’s no conclusive evidence that any supplement can eliminate cellulite.
Q 5. Does dry brushing really help with cellulite, and how does it work?
Ans. Dry brushing may help to exfoliate the skin and improve circulation, which could temporarily reduce the appearance of cellulite. It’s not a cure but can be part of a skincare routine.
Q 6. How does pregnancy affect cellulite, and will it go away postpartum?
Ans. Pregnancy can lead to weight gain and hormonal changes that may increase the visibility of cellulite. Postpartum weight loss and hormonal stabilization can reduce its appearance, but it may not go away completely.
Q 7. Is it true that smoking can worsen cellulite, and if so, why?
Ans. Smoking can affect circulation and reduce collagen production, leading to weaker skin and potentially worsening the appearance of cellulite.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cellulite is a common condition that affects many people, especially women. While it’s often associated with excess body fat, the reality is that it’s influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormones, and age.
Getting toned through regular exercise, particularly strength training and cardiovascular workouts, can help reduce the appearance of cellulite by improving muscle tone and reducing body fat. However, it’s important to remember that while these measures can help, they may not completely eliminate cellulite.
Diet also plays a significant role in managing cellulite. Consuming a balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and antioxidants can improve skin elasticity and collagen production, which can help reduce the appearance of cellulite. On the other hand, processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can contribute to cellulite.

Good day, and welcome to Fitthour. My name is Shubham Vijay, and I am a certified personal trainer and nutrition coach with 6 years of experience in the fitness industry. At Fitthour, we specialize in types of training, such as strength training, cardio, or HIIT, and our mission is to help clients achieve their fitness goals and improve their overall health.



