Introduction
Are you searching for an effective way to strengthen your forearms without needing a gym or fancy equipment? Look no further! In this article, we’re going to take a closer look at exercises that use your body weight to help you strengthen your forearms. Whether you’re an experienced fitness enthusiast or just starting your fitness journey, these exercises will help you build stronger, more resilient forearms.
SHOP FOR THE HAND GRIPPERS ON AMAZON
Strong forearms are not only beneficial for your athletic performance but also for your everyday tasks. In this article, we will introduce you to a variety of bodyweight forearm exercises that can be performed anywhere, ensuring you develop the grip strength and endurance your forearms deserve.
The Importance of Strong Forearms
Strong forearms might not be the first thing that comes to mind when you think of a well-rounded fitness regimen, but they play a vital role in your overall strength and functionality. Here are some compelling reasons why strong forearms matter:
- Enhanced Grip Strength: Your hands and fingers are your primary connection to the world. Everything you do, from opening a door to lifting weights, relies on your grip strength. Strong forearms contribute significantly to a powerful grip, making everyday tasks easier and more manageable.
- Reduced Risk of Injuries: Weak forearms are often associated with wrist and elbow injuries, like tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome. When your forearm muscles are strong, they provide better support to your joints, reducing the risk of such injuries.
- Improved Athletic Performance: In many sports, a strong grip is essential. Whether you’re a climber, golfer, or basketball player, forearm strength directly impacts your ability to perform at your best. It can give you an edge over the competition and help prevent injuries common in these sports.
- Functional Fitness: Strong forearms are essential for performing daily activities like carrying groceries, opening jars, and moving furniture. If you’ve ever struggled with these tasks, you’ll appreciate the value of forearm strength.
- Balanced Musculature: Achieving a well-rounded physique requires attention to all muscle groups, including the forearms. Neglecting your forearms can lead to muscle imbalances, which may result in joint pain and poor posture.
- Endurance and Stamina: Strong forearms can contribute to your overall endurance, allowing you to perform tasks for more extended periods without tiring quickly. This is beneficial in both athletic endeavors and daily life.
- Versatility in Workouts: If you’re into strength training, strong forearms allow you to perform exercises like deadlifts, pull-ups, and rows more effectively. These compound movements target multiple muscle groups and are essential for building overall strength.
- Injury Recovery: If you’ve experienced a forearm or wrist injury in the past, developing forearm strength can aid in your rehabilitation and prevent future issues.
SHOP FOR THE RESISTANCE BAND ON AMAZON
Strong forearms are not only beneficial but also essential for a well-rounded, functional, and injury-resistant body.
Anatomy of the Forearms

The forearms are a critical part of the upper limbs, connecting the elbow to the wrist and playing a central role in the intricate movements of the hands and fingers. Understanding the anatomy of the forearms is essential for anyone looking to strengthen these muscles or gain insight into their function. Let’s explore the key components of forearm anatomy.
Muscles of the Forearm
The forearm contains a complex network of muscles responsible for various movements, including flexion, extension, and rotation of the wrist and fingers. These muscles are generally categorized into two main groups: the flexors and the extensors.
Flexor Muscles
- Flexor Carpi Radialis: This muscle is located on the anterior (front) side of the forearm and is responsible for flexing the wrist.
- Flexor Carpi Ulnaris: Situated on the medial (inner) side of the forearm, this muscle also aids in wrist flexion.
- Palmaris Longus: This thin muscle runs along the inner part of the forearm, contributing to wrist flexion.
- Flexor Digitorum Profundus: This muscle flexes the fingers and is positioned deep within the forearm.
- Flexor Digitorum Superficialis: Located just above the deep flexor, it assists in flexing the fingers but acts more superficially.
- Flexor Pollicis Longus: Responsible for thumb flexion, this muscle is situated on the front side of the forearm.
- Pronator Teres: Found on the inner side of the forearm, it assists in pronation of the forearm (turning the palm downward).
Extensor Muscles
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus and Brevis: These muscles, located on the outer side of the forearm, are responsible for extending the wrist.
- Extensor Carpi Ulnaris: Situated on the outer side of the forearm, this muscle helps extend and adduct the wrist.
- Extensor Digitorum: Extending the fingers is its primary function, found on the dorsal (back) side of the forearm.
- Extensor Digiti Minimi: This muscle aids in extending the pinky finger.
- Extensor Indicis: Responsible for extending the index finger, it is less prominent.
- Supinator: Located deep in the forearm, it assists in supination, the movement that turns the palm upward.
- Abductor Pollicis Longus and Extensor Pollicis Brevis: These muscles extend the thumb and are located on the back of the forearm.
Tendons and Ligaments
Tendons are tough, fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones. In the forearm, these tendons play a crucial role in transmitting the force generated by muscles to the wrist and fingers, enabling movement. For example, the tendons of the wrist flexor and extensor muscles extend into the hand, allowing you to grasp, release, and manipulate objects with precision.
SHOP FOR THE PULL-UP BAR ON AMAZON
Ligaments in the forearm provide stability to the joints, preventing excessive movements that could lead to injury. The most significant ligaments in the forearm are found at the wrist joint, helping to maintain its integrity and protect against hyperextension or excessive flexion.
Nerves and Blood Supply
The forearm also contains essential nerves and blood vessels. The median nerve, ulnar nerve, and radial nerve run through the forearm, providing sensory and motor functions to the hand and fingers. Proper circulation is maintained by the radial and ulnar arteries, which supply oxygen and nutrients to the forearm muscles and surrounding tissues.
Understanding the anatomy of the forearms is fundamental to appreciating the intricacies of their function. The interplay of muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels in this area allows for the wide range of movements and dexterity we rely on in our daily activities.
Top 10 Bodyweight Forearm Exercises
Bodyweight forearm exercises are a great way to strengthen your forearms without any equipment. They can be done anywhere, at any time, and they can be modified to make them more or less challenging.
Here are the top 10 bodyweight forearm exercises:
1. Wrist Flexor Stretch
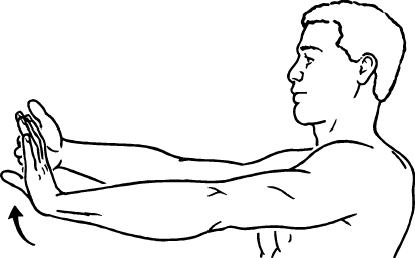
This exercise increases forearm flexibility and prepares your muscles for more challenging workouts.
How to Perform: Extend your arm in front of you, palm facing up. With your other hand, gently pull your fingers back. Hold for 20-30 seconds. Repeat on the other hand.
Tips: Perform this stretch before and after your forearm workouts to prevent injuries and enhance flexibility.
2. Chaturanga

Chaturanga is a yoga pose that engages your forearms and strengthens your core and upper body.
How to Perform: Start in a plank position, then slowly lower your body down, keeping your elbows close to your sides. Hold for a few seconds, then push back up.
Tips: Maintain a straight line from head to heels and engage your core throughout the movement. If this is challenging, start with knee push-ups and work your way up to Chaturanga.
3. Hand Squeezes

Hand squeezes enhance grip strength, and all you need is a stress ball or tennis ball.
How to Perform: Hold the ball in your hand and squeeze it as tightly as you can. Release and repeat for 15-20 squeezes on each hand.
Tips: Perform hand squeezes during short breaks in your day to consistently work on your grip strength.
4. Finger Extensions
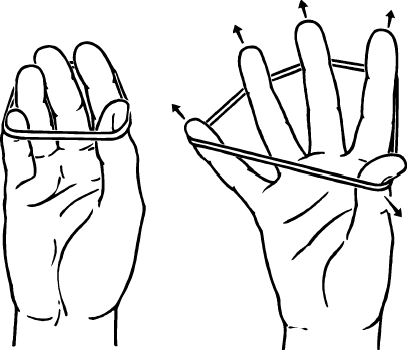
This exercise improves finger dexterity using rubber bands.
How to Perform: Place a rubber band around your fingers. Spread your fingers apart against the resistance of the band and then relax. Repeat 15-20 times on each hand.
Tips: Use bands of varying resistance to gradually increase the challenge.
5. Crab Walk

The Crab Walk is a fun and effective exercise that targets your forearms, triceps, and core.
How to Perform: Sit on the ground with your hands behind you and feet flat on the floor. Lift your hips off the ground and walk forward by moving your hands and feet in an alternating fashion.
Tips: Keep your hips elevated and your core engaged as you walk. You can vary the difficulty by extending the distance you walk or by introducing obstacles.
6. Fingertip Push-Ups
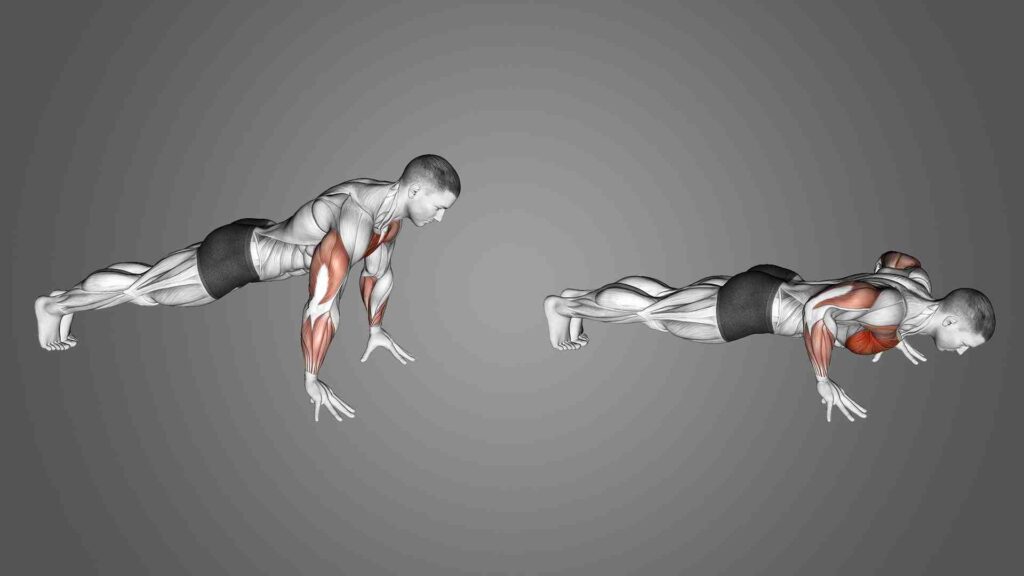
Fingertip push-ups not only strengthen your grip but also work your chest and shoulders.
How to Perform: Start in a push-up position, but place the weight on your fingertips instead of your palms. Perform push-ups with controlled movements.
Tips: Begin with knee push-ups or wall push-ups if fingertip push-ups are too challenging at first.
7. Forearm Plank
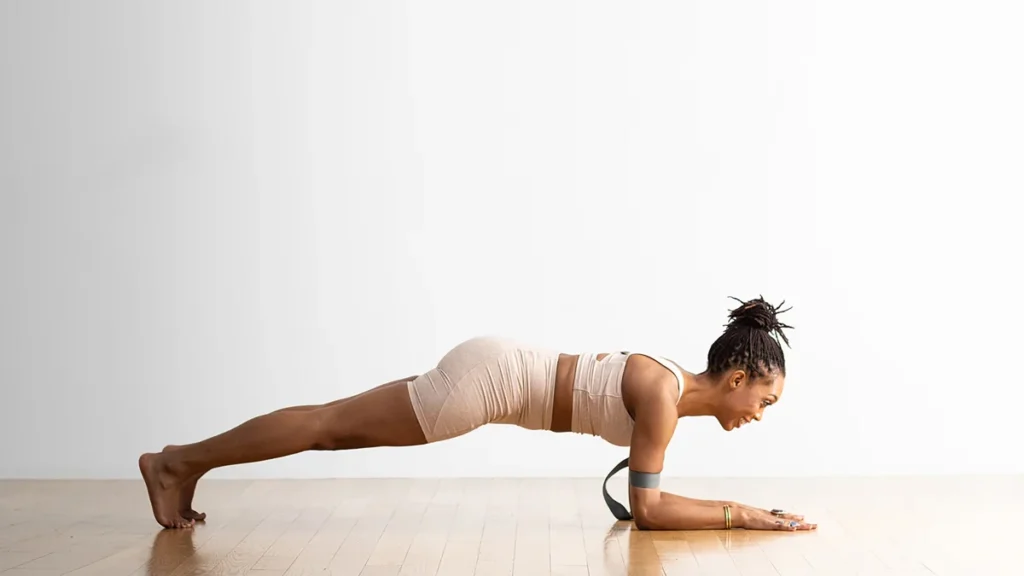

The forearm plank is an isometric exercise that engages both your core and forearms.
How to Perform: Get into a plank position, but rest on your forearms instead of your hands. Keep your body in a straight line.
Tips: Focus on maintaining proper form and gradually increase your plank duration.
8. Pull-Up Bar Hangs
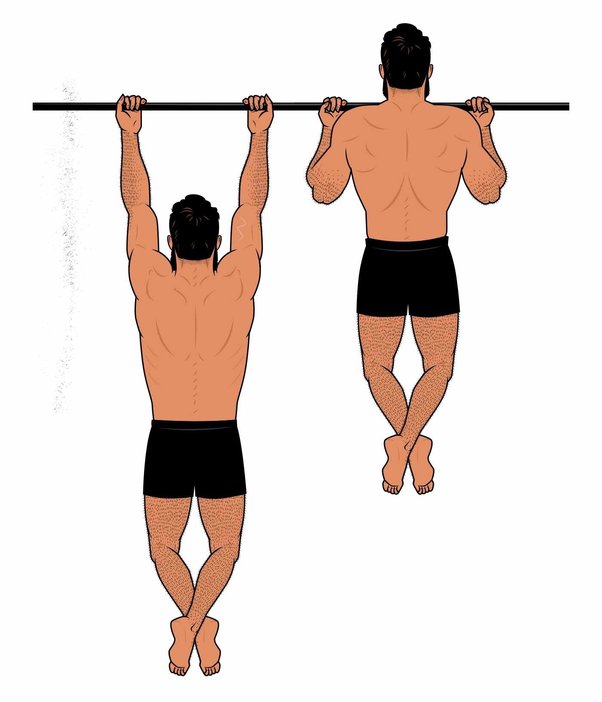
Hanging from a pull-up bar is a fantastic way to test and improve your grip strength.
How to Perform: Hang from a pull-up bar, keeping your shoulders engaged and your core tight. Aim to hang for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
Tips: Start with shorter hangs and increase the duration as your grip strength improves.
9. Towel Grip

Wrapping a towel around a pull-up bar challenges your grip strength on an unstable surface.
How to Perform: Drape a towel over a pull-up bar and grip the ends. Perform pull-ups or hangs with the towel.
Tips: Choose a sturdy bar and ensure the towel is securely in place.
10. Rock Climbing

Rock climbing is an adventurous way to build forearm strength, combining grip strength and strategy.
How to Perform: Find a climbing gym or a safe outdoor climbing spot and follow the guidance of experienced climbers or instructors.
Tips: Start with beginner routes and always use proper safety equipment and techniques.
SHOP FOR THE STRESS BALL ON AMAZON
Incorporate these exercises into your routine while maintaining proper form and gradually increasing the intensity to see significant improvements in your forearm strength and grip.
FAQs
Q1: Can I build significant forearm strength with bodyweight exercises alone?
Ans: Yes, you can build impressive forearm strength with bodyweight exercises. Consistency and proper form are key. Bodyweight exercises can be incredibly effective in developing forearm strength, especially when done consistently and with progressive overload.
Q2: How often should I work on my forearms?
Ans: Aim for 2-3 forearm workouts per week, allowing at least 48 hours of rest between sessions. This rest period is essential to allow your forearm muscles to recover and grow stronger.
Q3: Are there any dietary recommendations to support forearm muscle growth?
Ans: Consuming a well-balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients will aid muscle growth and recovery. Make sure to include lean protein sources, plenty of fruits and vegetables, and adequate hydration in your diet to support your overall fitness goals.
Q4: Are these exercises suitable for beginners?
Ans: Yes, most of these exercises are beginner-friendly. However, it’s essential to start with proper form and gradually increase the intensity. If you’re a beginner, it’s a good idea to start with lighter variations and focus on getting the techniques right before progressing to more challenging exercises.
Conclusion
Bodyweight forearm exercises are a versatile and effective way to build forearm strength without the need for a gym or specialized equipment. Whether you’re an athlete looking to improve performance or someone who wants to enhance daily activities, the exercises outlined in this guide will help you achieve your goals.
Remember, consistency is the key to success. Start with the exercises that match your fitness level and gradually progress as your strength improves.

Good day, and welcome to Fitthour. My name is Shubham Vijay, and I am a certified personal trainer and nutrition coach with 6 years of experience in the fitness industry. At Fitthour, we specialize in types of training, such as strength training, cardio, or HIIT, and our mission is to help clients achieve their fitness goals and improve their overall health.

