Introduction to Chest Growth
Chest growth is a topic of interest for many men, whether for aesthetic appeal, functional strength, or both. The chest is one of the most noticeable parts of the body, and a well-developed chest can contribute to a balanced physique and a strong, confident appearance.
The chest muscles, primarily the pectoralis major and minor, play a crucial role in various upper-body movements. They are involved in pushing movements, such as the bench press or push-ups, and they also stabilize the shoulder joint.
However, achieving significant chest growth involves more than just exercise. Nutrition plays a vital role in muscle development and recovery. Consuming the right nutrients can fuel your workouts, aid in muscle repair and growth, and help you achieve your chest development goals.
In this article, we will explore the best foods for chest growth, delve into the science of muscle development, and provide practical tips for incorporating these foods into your diet.
Anatomy of the Chest
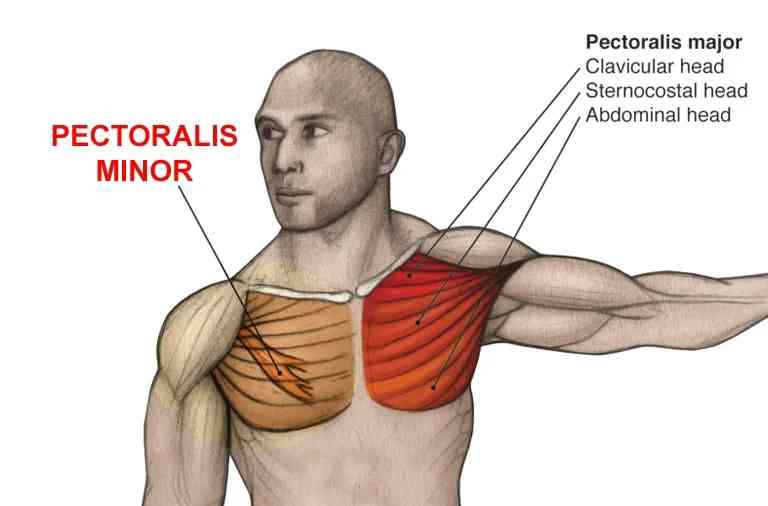
The chest, also known as the thoracic cavity, houses several vital organs, including the heart and lungs. However, when it comes to muscle growth and development, the primary muscles of interest are the pectoralis major and the pectoralis minor.
Pectoralis Major
The pectoralis major is the larger, more visible muscle in the chest. It’s fan-shaped and covers much of the front upper chest, starting from the breastbone and attaching to the upper arm. This muscle is responsible for movements such as pushing and pressing (like when you’re doing push-ups or bench press exercises).
Pectoralis Minor
The pectoralis minor is a smaller, triangular muscle located beneath the pectoralis major. It starts from the middle ribs and attaches to the shoulder blade. While it’s not as visible as the pectoralis major, it plays a crucial role in stabilizing the scapula, or shoulder blade.
Understanding the anatomy of the chest can help you target these muscles more effectively during your workouts.
Role of Nutrition in Muscle Growth
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in muscle growth and recovery. When you exercise, your body uses stored energy to fuel your workouts. After exercise, your body repairs the muscle fibers that have been broken down during your workout. Both these processes require nutrients from the food you eat.
Protein for Muscle Repair and Growth
Protein is a key nutrient for muscle growth. It provides the amino acids that your body uses to repair and rebuild muscle fibers. When you consume more protein than your body breaks down through natural processes and exercise, muscle protein synthesis occurs, leading to muscle growth.
Carbohydrates for Energy
Carbohydrates are your body’s primary source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is used immediately for energy or stored in your muscles as glycogen. During exercise, your body taps into these glycogen stores for energy. Consuming adequate carbohydrates ensures that you have the necessary energy for your workouts and prevents muscle breakdown.
Fats for Hormone Production
Fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, play a crucial role in hormone production, including testosterone, which is important for muscle growth. Fats also provide a dense source of calories, which can be beneficial if you need to increase your overall energy intake for muscle growth.
Vitamins and Minerals for Overall Health
Vitamins and minerals, while not directly responsible for muscle growth, contribute to overall health and help keep your body functioning optimally. They play various roles in the body, including energy production, bone health, immune function, and more.
Protein and Muscle Growth
Protein is a vital nutrient for muscle growth. It’s made up of amino acids, the building blocks of your muscles and body. Here’s how protein contributes to muscle growth:
Muscle Repair and Growth
When you work out, especially during resistance and strength training exercises, you create microscopic tears in your muscle fibers. This damage signals a repair process, where the body uses dietary protein to repair the damaged muscle fibers. This process helps the muscles to grow bigger and stronger.
Essential Amino Acids
20 different amino acids can form a protein, and nine that your body can’t produce on its own. These are called essential amino acids—we need to eat them because we can’t make them ourselves. In particular, the essential amino acid leucine plays a major role in initiating the process of muscle protein synthesis, which is the process your body uses to build new proteins.
Protein Sources
High-quality, lean protein sources are best for muscle growth. These include:
- Animal-based proteins: Such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. These are considered complete proteins as they contain all the essential amino acids your body needs.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Such as lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa. While most plant-based proteins are not complete proteins, you can combine different plant-based protein sources to get all the essential amino acids your body needs.
Protein Timing and Distribution
The timing and distribution of protein intake throughout the day can also impact muscle growth. Consuming a source of protein within a meal or snack every 3-4 hours is often recommended to stimulate muscle protein synthesis throughout the day.
Remember, while protein is crucial, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals also play significant roles in muscle growth and overall health.
Carbohydrates and Energy
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in your diet, especially when it comes to muscle growth and exercise performance. Here’s why:
Primary Source of Energy
Carbohydrates are your body’s primary source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is used immediately for energy or stored in your muscles and liver as glycogen. During exercise, your body taps into these glycogen stores for energy.
Fuel for Workouts
Having sufficient carbohydrates in your diet ensures that you have the necessary energy for your workouts. This is particularly important for high-intensity workouts, which rely heavily on glycogen stores.
Prevents Muscle Breakdown
When your carbohydrate intake is too low, your body may have to use protein for energy instead of muscle repair and growth. This can lead to muscle breakdown. Consuming adequate carbohydrates ensures that the protein you consume can be used for its primary role in muscle repair and growth.
Carbohydrate Sources
Good sources of carbohydrates include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. These foods not only provide energy but also deliver essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
Remember, while carbohydrates are important, they’re just one piece of the puzzle. Protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals also play significant roles in muscle growth and overall health.
Healthy Fats
Fats, particularly healthy fats, play a crucial role in muscle growth and overall health. Here’s why:
Hormone Production
Fats are involved in the production of hormones, including testosterone, which is important for muscle growth.
Energy Dense
Fats are the most energy-dense macronutrient, providing 9 calories per gram compared to 4 calories per gram for protein and carbohydrates. This makes them a valuable source of energy, especially for those trying to gain muscle mass.
Absorption of Vitamins
Fats also aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), which play various roles in the body, including bone health, immune function, and more.
Healthy Fat Sources
Healthy fats are primarily found in foods like:
- Avocados: They are rich in monounsaturated fats and also provide a good amount of fiber and vitamins.
- Fatty Fish: Such as salmon, trout, and sardines, are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fat.
- Nuts and Seeds: They are good sources of monounsaturated fats, and also provide protein, fiber, and various important nutrients.
- Olive Oil: It is high in monounsaturated fats, and using it in cooking is a good way to increase your intake of healthy fats.
Remember, while fats are important, they’re just one piece of the puzzle. Protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals also play significant roles in muscle growth and overall health.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals, while not directly responsible for muscle growth, contribute to overall health and help keep your body functioning optimally. They play various roles in the body, including energy production, bone health, immune function, and more. Here are some of the essential vitamins and minerals your body needs for muscle gain:
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a vital role in muscle health. Research has linked healthy vitamin D levels with stronger muscles and better posture.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A supports your vision, is essential for bone growth and development, and fights inflammation.
Iron
Iron helps your body make hemoglobin, which shuttles oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. So basically, iron helps keep energy high, muscle pumped, and breath control on point.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C helps you absorb iron, which is a #win for your weightlifting sesh. Healthy iron levels = more power to pump the other kind of iron.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a dominant antioxidant—a substance that helps you stay healthy by mopping up damaging free radicals (or unstable molecules).
B-Vitamins
B vitamins like B2 (Riboflavin), B3 (Niacin), and B6 play a crucial role in energy production and can help improve your performance during workouts.
Magnesium and Zinc
Magnesium is important for muscle function and works with calcium to support proper muscle contractions. Zinc is crucial for protein synthesis and helps your body repair muscles.
Remember, while vitamins and minerals are important, they’re just one piece of the puzzle. Protein, carbohydrates, and fats also play significant roles in muscle growth and overall health.
Meal Timing
Meal timing, or when you eat, can also impact muscle growth and recovery. Here’s why:
Pre-Workout Nutrition
Eating a balanced meal with protein, carbohydrates, and fats 1-2 hours before a workout can provide the energy you need to push through your workout. The protein in your pre-workout meal can help minimize muscle protein breakdown during the workout.
Post-Workout Nutrition
Eating a meal rich in protein and carbohydrates within an hour after your workout can maximize muscle protein synthesis and replenish glycogen stores, promoting muscle growth and recovery.
Protein Distribution
Consuming a source of protein within a meal or snack every 3-4 hours is often recommended to stimulate muscle protein synthesis throughout the day.
Nighttime Nutrition
Some research suggests that consuming a protein-rich snack before bed can stimulate muscle protein synthesis while you sleep, further promoting muscle growth.
What Muscles Do Bent Arm Dumbbell Pullovers Work?
Remember, individual needs can vary, and what works best for one person may not work as well for another. It’s always a good idea to experiment with different meal timings to see what works best for you.
Sample Meal Plan
Breakfast
- Scrambled Eggs: Made with 2 whole eggs and 2 egg whites, cooked in olive oil.
- Whole Grain Toast: 2 slices, with a spread of natural almond butter.
- Fruit: A banana or an apple for some healthy, natural sugars and fiber.
Mid-Morning Snack
- Greek Yogurt: A cup of plain Greek yogurt, which is high in protein.
- Mixed Berries: A handful of mixed berries for added fiber and antioxidants.
- Nuts: A small handful of almonds or walnuts for healthy fats.
Lunch
- Grilled Chicken Salad: A large salad with plenty of leafy greens, a grilled chicken breast, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and avocado. Dress with olive oil and lemon juice.
- Quinoa: A side of quinoa for a boost of whole grains and protein.
Afternoon Snack
- Protein Shake: A shake made with whey protein powder, almond milk, and a banana.
Dinner
- Salmon: A grilled salmon fillet for a dose of protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Sweet Potato: A baked sweet potato for complex carbohydrates.
- Steamed Vegetables: A side of steamed broccoli and carrots for vitamins and fiber.
Evening Snack
- Cottage Cheese: A cup of cottage cheese with a sprinkle of flaxseeds. Cottage cheese is slow-digesting, making it a good pre-bed snack.
Remember, this is just a sample meal plan and actual needs can vary based on individual goals, body size, age, gender, and level of physical activity. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making any major changes to your diet.
Exercises for Chest Growth
Many exercises can target your chest muscles and help you build a bigger and stronger chest. Some of the most effective ones are:
Flat Barbell Bench Press
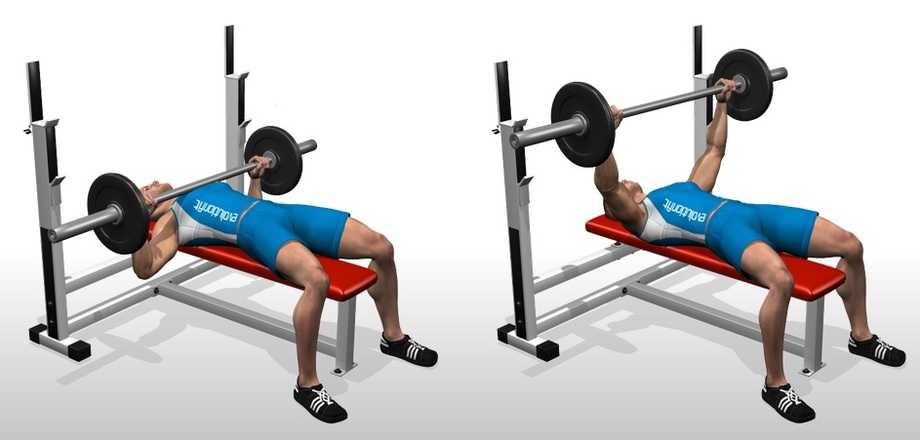

This is a classic exercise that allows you to move a lot of weight and work your entire chest. It also engages your triceps and shoulders. To perform it, lie on a flat bench and grip the barbell with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Unrack the bar and lower it to your chest, keeping your elbows tucked in. Press the bar back up until your arms are fully extended. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Incline Barbell Bench Press
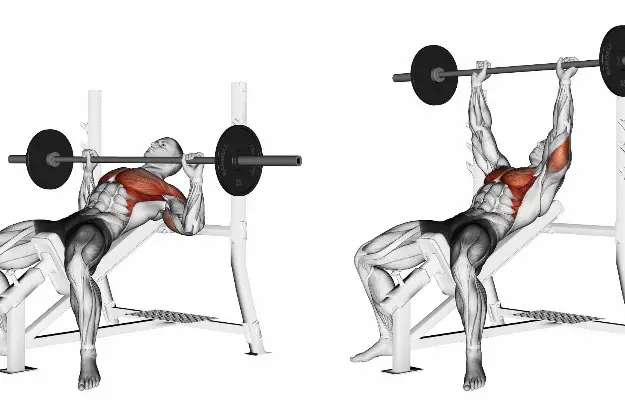
This is a variation of the flat bench press that targets the upper chest more. It also works your front deltoids and triceps. To perform it, set up a bench at an incline of about 30-45 degrees and lie on it. Grip the barbell with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart and unrack it. Lower the bar to your upper chest, keeping your elbows tucked in. Press the bar back up until your arms are fully extended. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Dumbbell Bench Press (Incline or Flat)
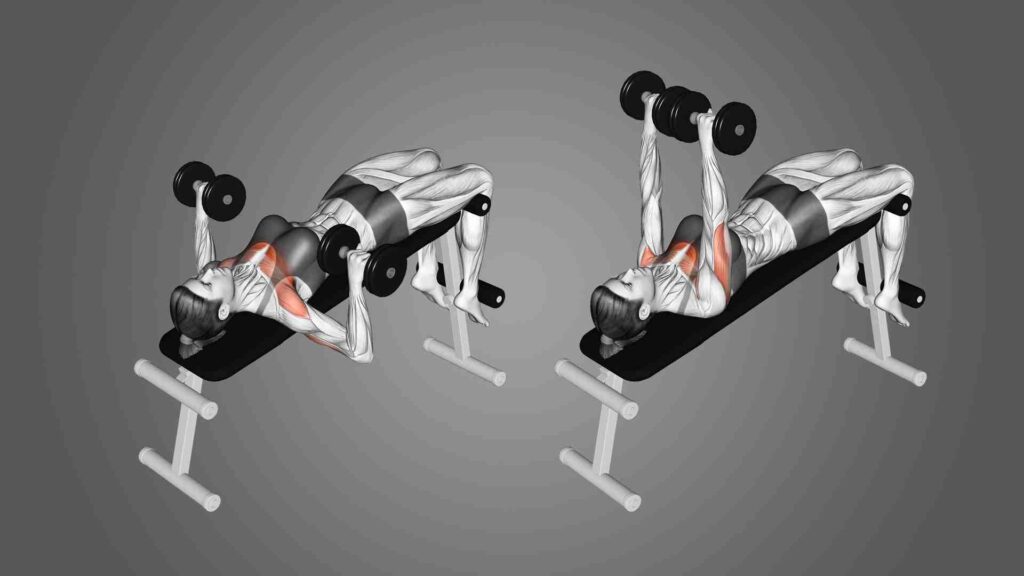
This is a dumbbell version of the bench press that allows you to have more range of motion and work each side of your chest independently. It also engages your stabilizer muscles more. You can perform it on a flat or an incline bench, depending on which part of your chest you want to emphasize. To perform it, lie on a bench and hold a dumbbell in each hand at chest level, with your palms facing forward. Press the dumbbells up over your chest until your arms are fully extended. Lower the dumbbells back to the starting position, keeping your elbows tucked in. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Dumbbell Flye (Flat or Incline)
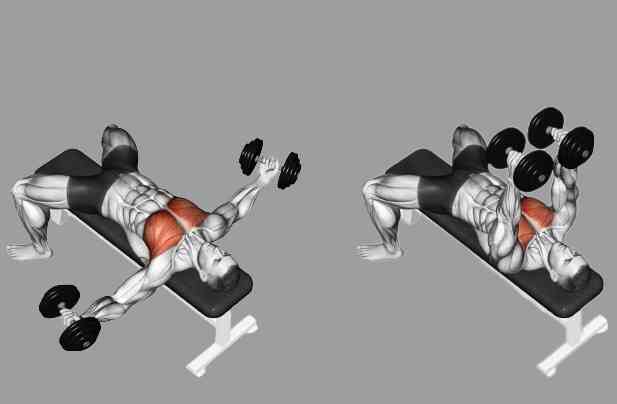

This is an isolation exercise that works your chest by stretching and contracting your pectoral muscles. It also works your front deltoids and biceps. You can perform it on a flat or an incline bench, depending on which part of your chest you want to target. To perform it, lie on a bench and hold a dumbbell in each hand at chest level, with your palms facing each other. Keeping your arms slightly bent, lower the dumbbells to the sides of your chest, feeling a stretch in your pecs. Bring the dumbbells back together over your chest, squeezing your pecs. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Dips
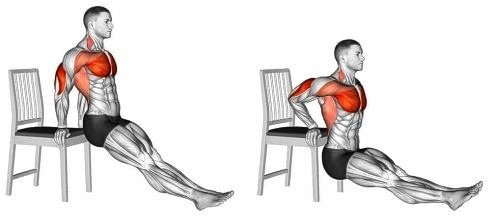
This is a bodyweight exercise that works your lower chest, triceps, and shoulders. It also improves your core stability and strength. To perform it, grab the parallel bars of a dip station and lift yourself up until your arms are fully extended. Lean your torso slightly forward and bend your knees. Lower yourself until your elbows are at a 90-degree angle, keeping your elbows close to your body. Push yourself back up to the starting position, extending your arms. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Does Skipping Rope Build Calves?
These are some of the best exercises for chest growth, but there are many others that you can try. You can also vary the intensity, volume, frequency, and rest periods of your chest workouts to optimize your results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chest exercises are important for building muscle, strength, and aesthetics. They can also improve your posture, confidence, and performance in other activities. There are many chest exercises that you can choose from, depending on your goals, preferences, and equipment availability. Some of the most effective ones are flat barbell bench press, incline barbell bench press, dumbbell bench press, dumbbell flye, and dips. You can also vary your chest workouts by changing the intensity, volume, frequency, and rest periods. By following a consistent and progressive chest training program, you can achieve a bigger and stronger chest.

Good day, and welcome to Fitthour. My name is Shubham Vijay, and I am a certified personal trainer and nutrition coach with 6 years of experience in the fitness industry. At Fitthour, we specialize in types of training, such as strength training, cardio, or HIIT, and our mission is to help clients achieve their fitness goals and improve their overall health.




