In the world of bodybuilding, nutrition plays a pivotal role in shaping one’s physique and performance. Among the myriad of supplements that have gained popularity in this arena, L-glutamine stands out for its unique benefits. L-glutamine, the most abundant amino acid in the body, has been the subject of numerous studies for its role in muscle recovery, protein synthesis, and immune function. This article delves into the science behind L-glutamine and explores why it’s a staple in many bodybuilders’ supplement stacks.
What is L-glutamine?
L-glutamine is an amino acid, which is the building block of protein. It’s the most abundant amino acid in the body, found in muscle tissue, plasma, and nearly every animal product. It’s created in the human body when the non-essential amino acid glutamate is broken down and binds with nitrogen-containing ammonia molecules.
L-glutamine plays a part in various bodily processes such as regulating protein synthesis and breakdown, BCAA metabolism, gut barrier maintenance, normal immune function, glucose formation, water transport, neurotransmission, and more. It’s also involved in muscle recovery as it helps repair skeletal muscles.
SHOP FOR THE L-GLUTAMINE SUPPLEMENT ON AMAZON
L-glutamine is considered “conditionally essential,” meaning that the body can produce enough to meet its needs under normal circumstances, but not always. Therefore, it’s necessary to consume dietary sources of glutamine under certain circumstances when the body is under extreme duress.
The form of glutamine found in foods and supplements is L-glutamine. Some supplements list it as L-glutamine, but others simply use the broader term glutamine. While L-glutamine is used to make proteins and perform other functions, D-glutamine appears to be relatively unimportant in living organisms.
In summary, L-glutamine is an important amino acid that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, particularly in protein synthesis, immune function, and intestinal health. It’s found in many foods and can also be produced naturally by your body.
Role of L-glutamine in the Body
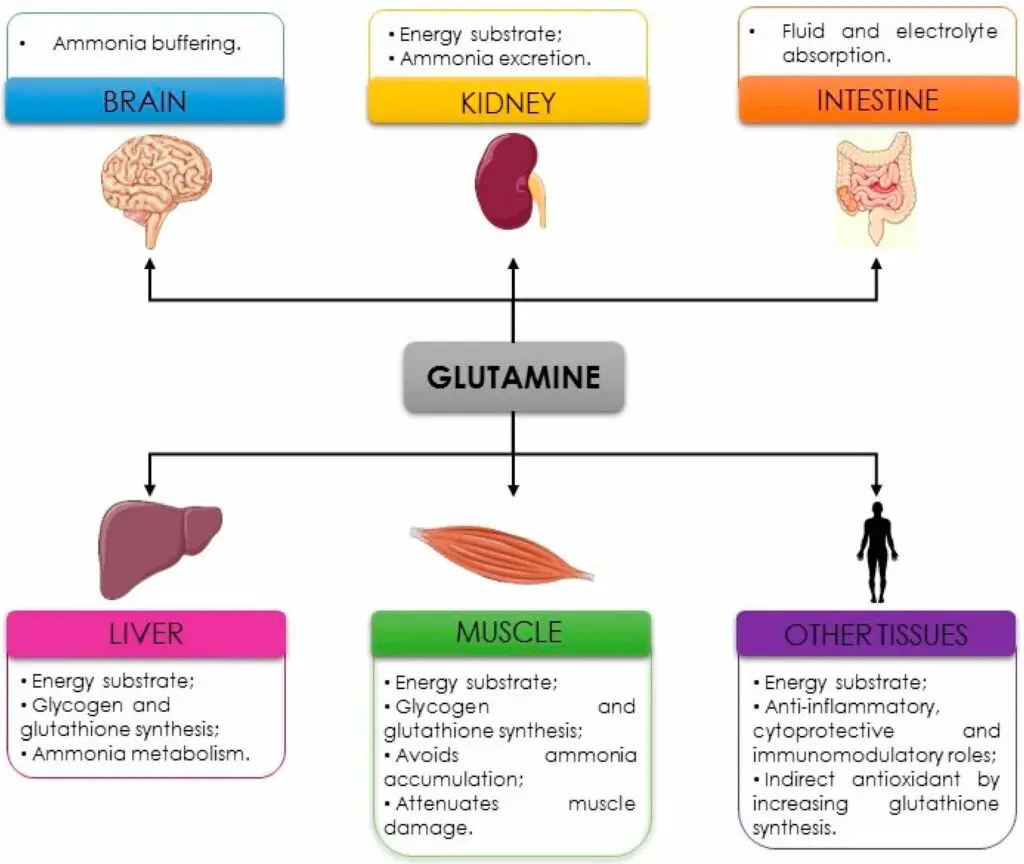
L-glutamine plays a crucial role in various bodily functions:
- Protein Synthesis: L-glutamine is involved in protein synthesis as it serves as a building block of protein. It’s also involved in the synthesis of lipids in certain cells.
- Immune System Support: L-glutamine supports the immune system. It helps maintain secretory IgA, which prevents the attachment of bacteria to mucosal cells. It also appears to be required to support the proliferation of mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes, as well as the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma).
- Intestinal Health: L-glutamine has a special role in intestinal health. It helps in maintaining the gut barrier and regulating the acid-base balance within the kidneys.
- Energy Production: L-glutamine helps the body in the formation of energy. It’s also involved in the metabolic process occurring in the kidney and the liver.
- Transporting Substances: Proteins, which L-glutamine is a part of, serve functions such as transporting substances in the blood and fighting off harmful viruses and bacteria.
- Donating Carbon and Nitrogen Atoms: L-glutamine is said to have the capability of donating carbon and nitrogen atoms in various processes such as anabolic, metabolic, cell divisions, etc.
- Neurotransmitter: As a neurotransmitter, L-glutamine is essential for healthy brain functioning. It may be needed for normal brain function.
- Detoxification: L-glutamine helps in detoxifying the liver and kidneys. It’s key for ridding the body of excess ammonia.
- Healing After Major Injuries: L-glutamine plays a beneficial role in healing after major injuries like burns, severe wounds, and infections associated with surgeries.
- Easing Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Your digestive system is lined with mucosa, which is protected by glutamine. Researchers have found that patients suffering from gastrointestinal issues may have lower levels of glutamine. An L-glutamine supplement may help ease symptoms and provide much-needed relief.
SHOP FOR THE L-GLUTAMINE GUMMIES ON AMAZON
In summary, L-glutamine is an important amino acid that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, particularly in protein synthesis, immune function, and intestinal health. It’s found in many foods and can also be produced naturally by your body.
L-glutamine and Muscle Recovery
L-glutamine plays a vital role in muscle recovery, especially after intense workouts. Here’s how:
- Muscle Repair and Growth: L-glutamine is essential for muscle repair and growth. It helps to reduce muscle soreness and promotes muscle recovery. It also facilitates muscle protein synthesis, which is essential for muscle recovery and muscle building.
- Prevents Muscle Breakdown: L-glutamine inhibits muscle mass breakdown and improves protein metabolism, thus improving exercise-induced muscle soreness. This is particularly beneficial after intense workouts when muscle tissues are stressed and need repair.
- Hydration and Recovery: Supplementing with L-glutamine can improve muscle hydration, which is crucial for recovery after intense weight training sessions.
- Production of Growth Hormone: L-glutamine can increase the production of human growth hormone (HGH), which is essential for muscle growth, repair, and overall rejuvenation.
- Post-Workout Recovery: L-glutamine is considered a great supplement for muscle recovery post-workout. In times of severe physical stress or trauma, such as prolonged workout durations, and high-intensity training, glutamine stores may become depleted, making it necessary to replenish and restore through supplementation.
In summary, L-glutamine is a key amino acid that aids in muscle recovery by preventing muscle breakdown, promoting muscle growth, and speeding up recovery after intense workouts.
L-glutamine and the Immune System
L-glutamine plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system:
- Fuel for Immune Cells: L-glutamine is utilized at a high rate by cells of the immune system and is required to support optimal lymphocyte proliferation and the production of cytokines by lymphocytes and macrophages.
- Gut Health and Immunity: Around 70–80% of your immune system is located in your gut. L-glutamine can improve your overall gut health, including your immune system. With a stronger immune system, you’ll be able to fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
- Support During Illness or Injury: Most people benefit from taking glutamine when their immune system is weakened or for healing a major wound like a burn or after surgery. For that reason, supplementing with L-glutamine could help improve immune system function and speed recovery.
- Detoxification: L-glutamine helps in detoxifying the liver and kidneys, which is key for ridding the body of excess ammonia. This process is important for maintaining a healthy immune system.
In summary, L-glutamine is an important amino acid that supports the immune system in various ways, from fueling immune cells to maintaining gut health and aiding recovery during illness or injury.
When to Supplement With L-glutamine
L-glutamine is considered “conditionally essential,” which means that your body can usually produce enough of it, but in times of stress or illness, you may need to get it from your diet or supplements. Here are some situations when you might consider supplementing with L-glutamine:
- Post-Workout Recovery: After intense workouts, the body’s glutamine levels can be depleted. Supplementing with L-glutamine can help replenish these levels, support muscle recovery, and reduce soreness.
- During Illness or After Surgery: If your immune system is weakened or you’re healing from a major wound like a burn or surgery, you might benefit from taking L-glutamine.
- Chronic Illness or Trauma: Reduced glutamine due to chronic illness or trauma could result in symptoms like diarrhea or “leaky gut.” In these cases, supplementing with L-glutamine may be helpful.
As for the best time to take L-glutamine supplements, it’s generally recommended to take them half an hour after a workout, in between two workout sessions, soon after you wake up in the morning, or half an hour before a meal.
Remember, it’s always important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Benefits and Drawbacks of L-glutamine Supplementation
L-glutamine supplementation has several benefits, but it also has potential drawbacks. Here’s a summary:
Benefits:
- Muscle Recovery: L-glutamine can aid in muscle recovery after intense workouts by reducing muscle soreness and promoting muscle growth.
- Immune System Support: L-glutamine supports the immune system and can enhance its ability to deal with stress, such as during intense workouts.
- Gut Health: L-glutamine plays a special role in maintaining gut health and integrity. It’s beneficial for people with certain gastrointestinal issues.
- Brain Health: L-glutamine is essential for healthy brain functioning and may be needed for normal brain function.
Drawbacks:
While L-glutamine is generally safe for most people, some individuals may experience side effects or may not be suitable for supplementation:
- Side Effects: Some people have reported side effects such as constipation and bloating.
- Health Conditions: Supplements may not be suitable for those who have a sensitivity to monosodium glutamate, epilepsy, bipolar disorder, or liver disease. They may also interfere with antiseizure medications.
- Overuse: While L-glutamine is beneficial, overuse can lead to an imbalance in the body’s nitrogen balance.
Remember, it’s always important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen. They can provide personalized advice based on your health history and current medications.
FAQs
Q 1. What foods are high in L-glutamine?
Ans. Foods that are high in L-glutamine include fish and seafood, dairy, meat, eggs, beans, tofu, dark leafy greens, red cabbage, nuts, and seeds. Other sources include eggs (4.4% or 0.6g per 100g of eggs), beef (4.8% or 1.2g per 100g of beef), skim milk (8.1% or 0.3g per 100g of milk), tofu (9.1% or 0.6g per 100g of tofu), white rice (11.1% or 0.3g per 100g of rice), and corn (16.2% or 0.4g per 100g of corn).
Q 2. How much L-glutamine should I take for muscle recovery?
Ans. The most effective dose of L-glutamine to help with faster recovery and reduce exercise-induced muscle soreness is a conventional dose of 5-10g per day. For bodybuilding, the dosage of Glutamine per day is generally 10-20 grams.
Q 3. Can I take L-glutamine on an empty stomach?
Ans. Yes, L-Glutamine is most effective when taken on an empty stomach without food. It is best to take glutamine supplements about 10-15 minutes before a meal.
Q 4. Is it safe to take L-glutamine every day?
Ans. Yes, it is safe to take L-glutamine every day. Glutamine is an amino acid that is naturally produced in the body and found in many foods.
Q 5. Does L-glutamine interact with any medications?
Ans. Yes, L-glutamine may interact with certain medications. It’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Q 6. What are the signs of L-glutamine deficiency?
Ans. Signs of L-glutamine deficiency can include increased infections, weight loss, and bowel changes. Other symptoms can include trouble concentrating, mental exhaustion, insomnia, and low energy.
Q 7. Can L-glutamine help with weight loss?
Ans. Yes, L-glutamine may promote weight loss by altering the composition of the gut microbiome, decreasing inflammation, and improving insulin sensitivity. It may also help reduce sugar cravings, which can aid in weight loss.
Q 8. Does cooking destroy L-glutamine?
Ans. Yes, cooking can destroy L-glutamine, particularly in vegetables.
Q 9. Can L-glutamine help with sleep?
Ans. Yes, L-glutamine has been associated with stress reduction, which is crucial in promoting relaxation and preparing the body for sleep. It can also have a calming effect and counteract stress symptoms, assisting in drifting off to sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, L-glutamine, the most abundant amino acid in the body, plays a pivotal role in various bodily functions, particularly in protein synthesis, immune function, and intestinal health. It’s essential for muscle recovery, making it a popular supplement among bodybuilders. While the body can usually produce enough L-glutamine, supplementation may be beneficial in times of stress, illness, or after intense workouts.
However, like any supplement, it’s important to use L-glutamine responsibly and consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new regimen. As we continue to learn more about this powerful amino acid, its potential applications in health and fitness are sure to expand.

Good day, and welcome to Fitthour. My name is Shubham Vijay, and I am a certified personal trainer and nutrition coach with 6 years of experience in the fitness industry. At Fitthour, we specialize in types of training, such as strength training, cardio, or HIIT, and our mission is to help clients achieve their fitness goals and improve their overall health.


